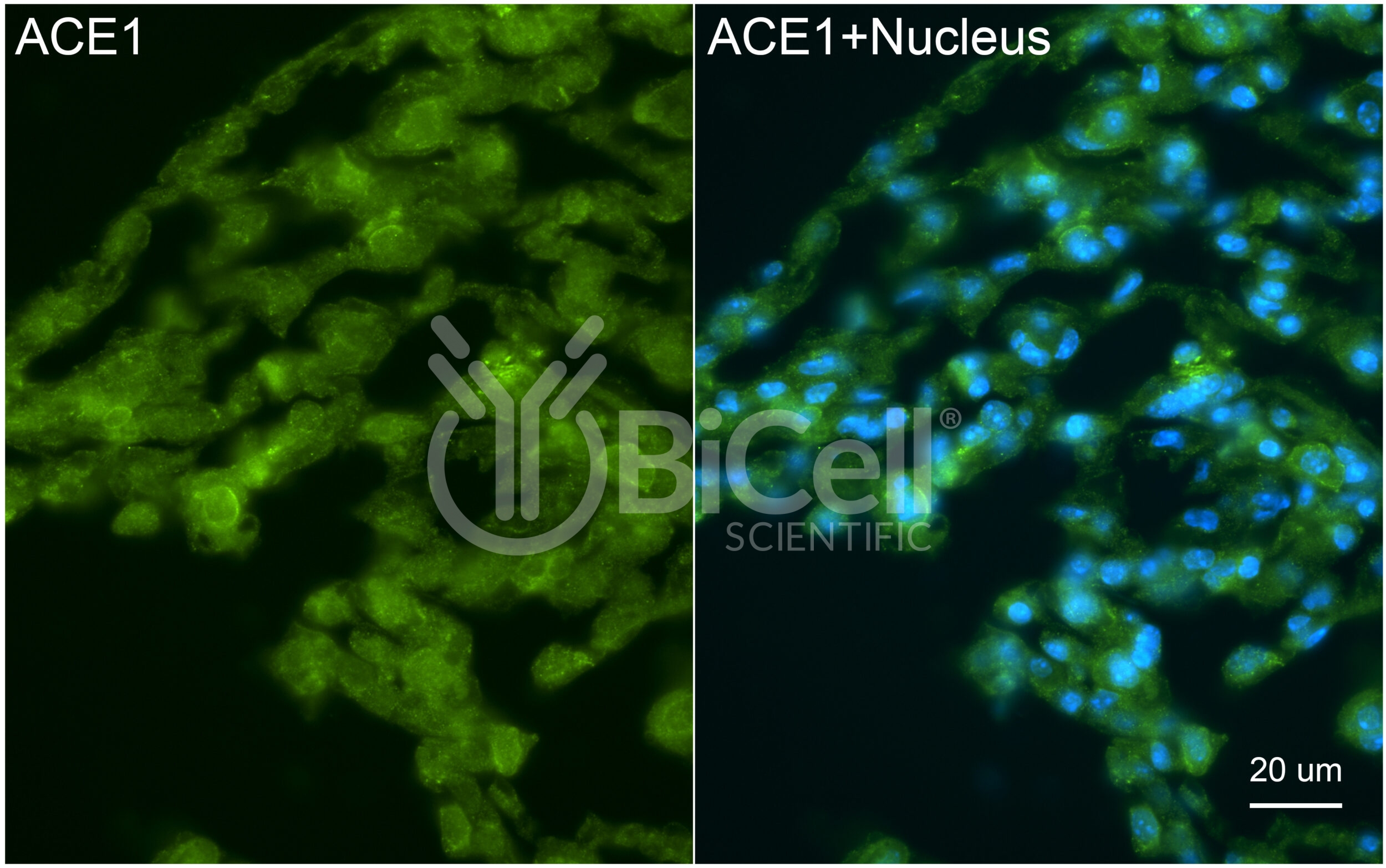
ACE1 (ACE or CD143) Antibody
Description
Anti-ACE1 (ACE or CD143) antibody is validated on mouse tissue and recommended for immunofluorescence labeling, IHC, or western blot of materials from human and rodent tissues. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, ACE1 or CD143) is encoded by the ACE gene in human. ACE is a central component of the reninangiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. ACE is a single-pass type I membrane protein. The extracellular domain of ACE can be cleaved from the transmembrane domain to circulate as soluble ACE or sACE. The ACE gene encodes two isozymes. The somatic isozyme, expressed in the endothelium of many epithelial tissues, has longer extracellular domain, whereas the germinal isozyme, expressed only in sperm, has truncated extracellular domain. This antibody was raised against the extracellular domain of somatic ACE isozyme and can recognize both soluble and membrane bound ACE.
| Application: | Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot |
|---|---|
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Concentration: | 0.25 mg/ml |
| Conjugation: | Unconjugated |
| Host: | Rat |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide (16-aa) derived from the N-terminal extracellular region of mouse ACE protein |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Purification: | Affinity Chromatography |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Species Homology: | Synthetic peptide sequence is identical to rat sequence (showing 93.8% homology to human sequence) |
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS, pH 7.2, 0.1% Sodium Azide |