ROMK (Kir1.1 or KCNJ1) Antibody
Description
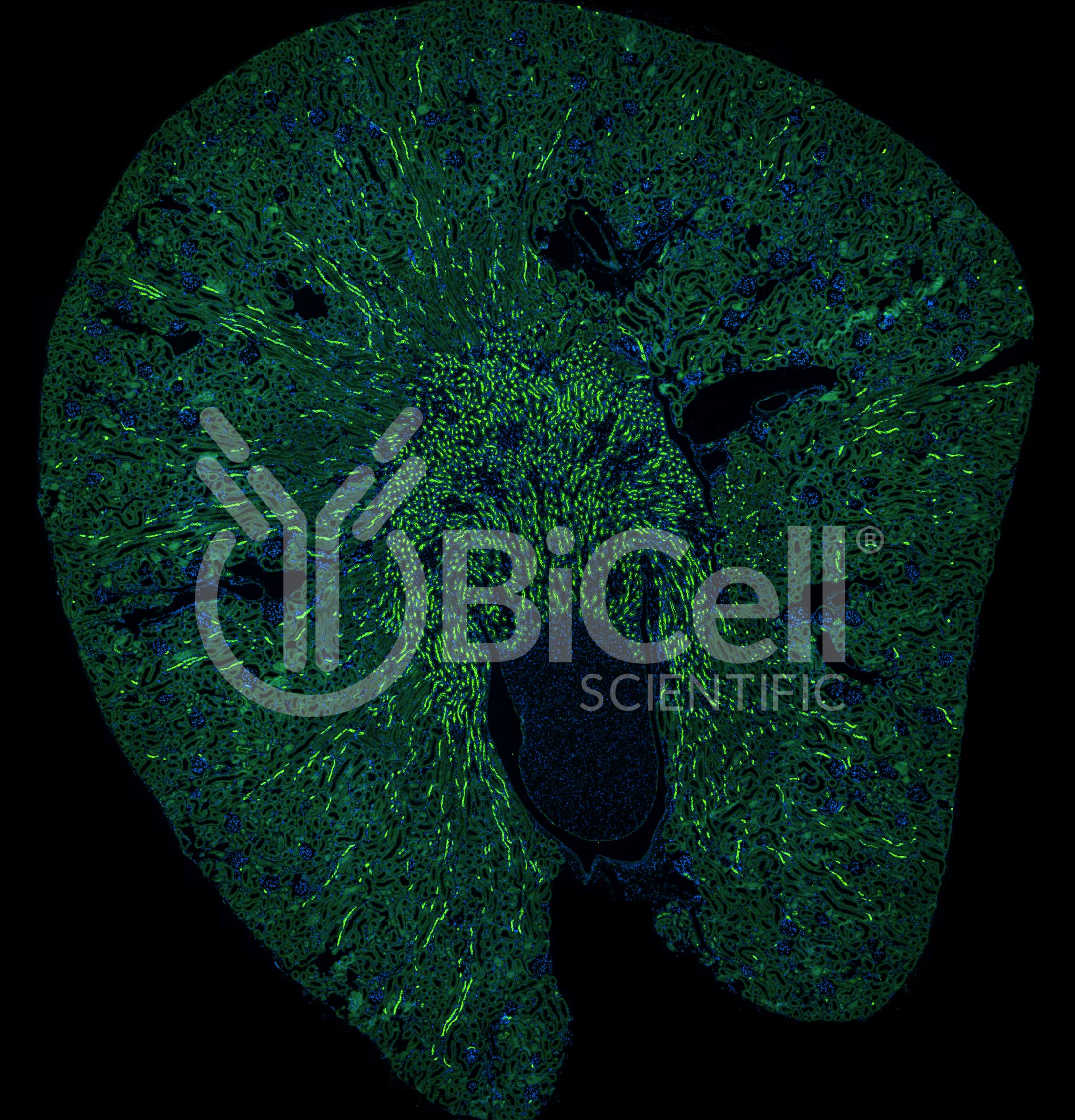
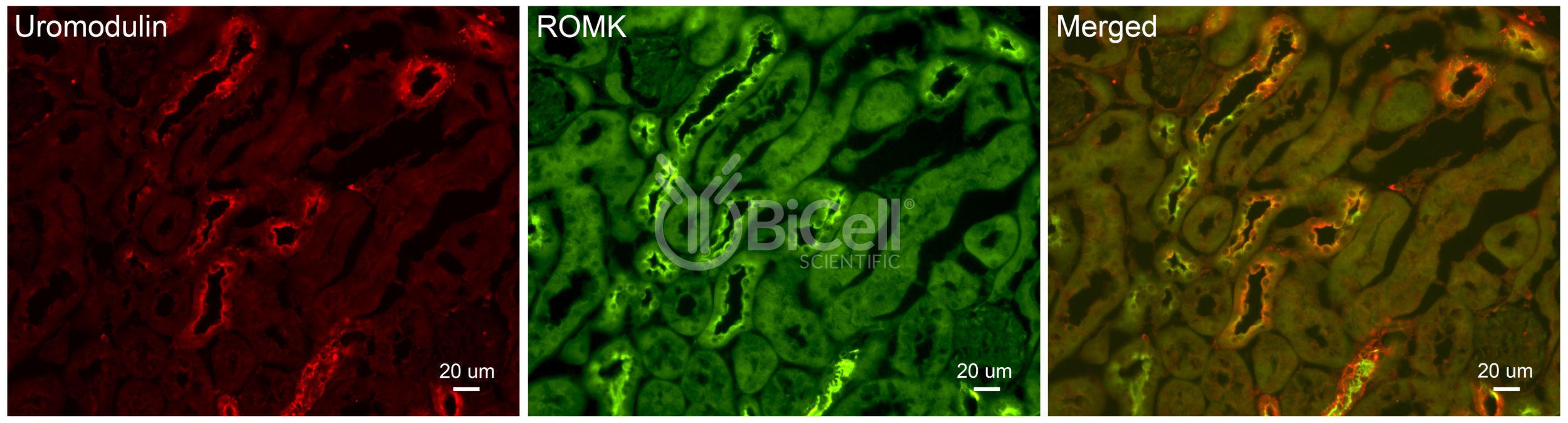
Anti-ROMK (Kir1.1 or KCNJ1) antibody is validated on mouse tissue and recommended for immunofluorescence labeling, IHC, or western blot of materials from rodent and human tissues. The Renal Outer Medullary Potassium channel (ROMK) is an ATP-dependent potassium channel that transport potassium across cell membrane. ROMK is also known as Kir1.1 or KCNJ1 (inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, subfamily J, member 1). ROMK is encoded by the KCNJ1 gene in human. ROMK consists in three transmembrane domains and the pore forming motif is within the 2nd transmembrane domain. ROMK is highly expressed in the thick ascending limbs of the kidney tubules. Mutations in ROMK cause an autosomal recessive disease known as Bartter syndrome (OMIM 600359), which is characterized by salt wasting, hypokalemic alkalosis, hypercalciuria, and low blood pressure.
| Application: | Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot |
|---|---|
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Concentration: | 0.25 mg/ml |
| Conjugation: | Unconjugated |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide (19-aa) derived from the C-terminal region of mouse ROMK protein |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Purification: | Affinity Chromatography |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Species Homology: | Synthetic peptide sequence is identical to rat sequence (showing 84.2% homology to human sequence) |
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS, pH 7.2, 0.1% Sodium Azide |